Open Journal of Tropical Medicine
Tropical Regions and the Concept of ‘International Medicine’- Measures that the Government Might Need to Take to Respond to Natural Disasters
SP.MSC, International Medical and Scientific Coordinator, Leg Clinics Net (Klinik Piano AG), Department of General Medicine, Instrumental Lymph Drainage Approaches, Switzerland
Author and article information
Cite this as
Jeyaretnam J. Tropical Regions and the Concept of ‘International Medicine’- Measures that the Government Might Need to Take to Respond to Natural Disasters. Open J Trop Med. 2025; 9(1): 007-009. Available from: 10.17352/ojtm.000029
Copyright License
© 2025 Jeyaretnam J. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.Insufficient supply and sanitation services affect the lives of billions of people in developing countries. The situation is exacerbated during natural disasters because existing infrastructure is destroyed and scarce resources are diverted to crisis management and subsequent reconstruction. By comparison, many developed countries have preventative measures in place to reduce the risk of damage as well as strategies and measures to mitigate the impact of the next disaster. In these situations, environmental health professionals from governmental and non-governmental organizations can play an important role in disaster prevention, mitigation, and response. Nevertheless, the success of environmental health programs depends on existing social inequalities. In many developing countries, the poorest and most vulnerable people already live in a situation of poor water supply and sanitation, which is exacerbated by natural disasters.
The tropics are the regions of the earth that lie approximately in the center of the globe. Those regions are located between the latitudes of the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn. The tropics include the equator and North America, South America, Africa, Asia, and Australia [1].
International medicine also referred to as geographic or global health, is a healthcare field that addresses health across regional or national boundaries, usually with a public health focus.
Natural disasters can occur anytime and anywhere: All governments must take precautions and provide emergency aid [2].
Thousands of people lose their homes or lives to destructive natural disasters such as floods, earthquakes, or hurricanes every year. Climate change has significantly increased the frequency of natural disasters in recent years, and more and more people, including those in Europe, are affected by these powerful natural events. Especially in economically vulnerable countries in Africa, South America, and Asia, unpredictable natural events sometimes threaten numerous people’s lives and can become a humanitarian crisis.
Municipalities and institutions in vulnerable areas are often not adequately prepared for natural disasters, making the impact even more devastating. The government must support people with on-the-ground assistance programs to take preventive and protective measures for future natural disasters. The state must not only be able to provide rapid emergency aid in the event of a disaster but also raise awareness of the impending dangers among the population through training and exercises, thus helping to reduce damage and suffering in the event of a disaster [3].
Unfortunately, more tropical countries are prone to fall vulnerability to natural disasters. One always speaks of a natural disaster when an enormous natural event such as floods, forest fires, or volcanic eruptions has destructive and far-reaching effects on the earth’s surface, people, and other living creatures. In contrast, one speaks of an environmental disaster when the event is caused by humans themselves, as in the case of the Chornobyl nuclear disaster or an oil spill in the open sea.
Discussion
However, a natural event alone is not a disaster, primarily if the event occurs far from inhabited areas, For example, a glacier collapse or an avalanche in an uninhabited region does not pose an immediate danger to people. However, because such huge events are challenging to control and can quickly become a hazard due to their high energy, they are forces of nature that must be taken seriously.
One of the reasons natural disasters are so devastating is that they usually occur unpredictably, and the consequences are also unpredictable. However, some natural events, such as hurricanes, can be detected earlier than others. As a rule, however, it is tough to make provisions for such exceptional situations. There are indeed early warning systems that detect special natural events such as earthquakes. However, these usually only become effective immediately before the disaster. Only warnings can be issued during this short period, and initial protective measures can be initiated. Nonetheless, it is an essential task of government and regulatory agencies and authorities. Still, it is up to the government to facilitate disaster prevention when such disasters occur to repair or compensate for the damage.
The types of natural disasters:
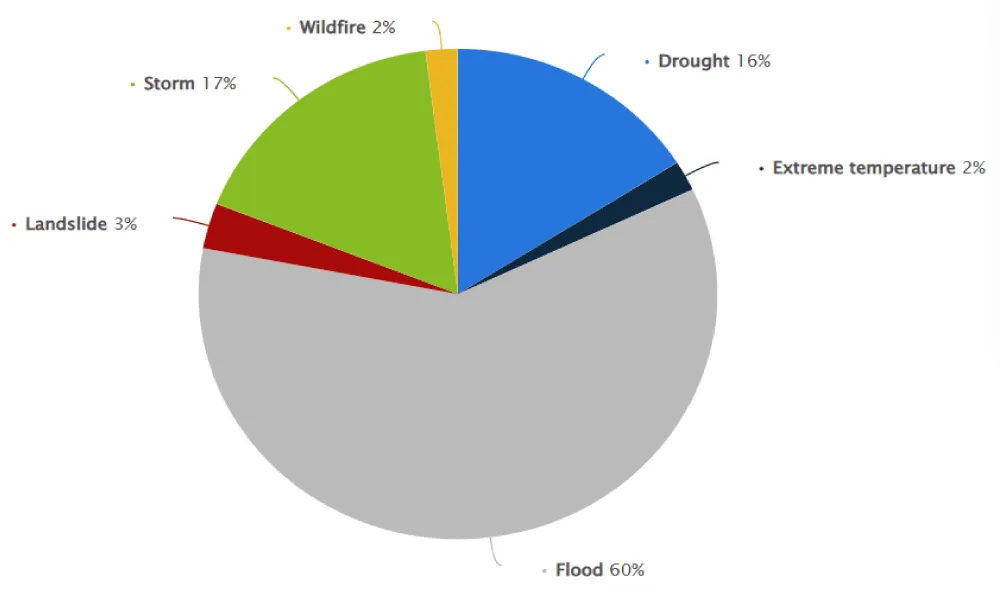
General natural disasters occur in different forms, each requiring different emergency responses. People need additional supplies after a flood than after or during a drought. However, natural events have one thing in common: their consequences are devastating. People often lose loved ones and all their belongings. All governments must be able to work on the ground to get people the help they need in their particular situations (Figure 1).
There are several types of natural disasters, some of which vary significantly in frequency. The most common natural disasters include floods, storms, earthquakes, and droughts. Natural disasters also include forest fires, volcanic eruptions, or landslides, although these occur less frequently. As a result of climate change, the frequency of natural disasters such as floods and droughts is increasing. In contrast, tectonic events such as volcanic eruptions or earthquakes remain constant.
The frequency of annual natural disasters has increased sharply in recent years: According to the World Meteorological Organization, yearly natural disasters have increased fivefold over the past 50 years. Since 2012, there have been more than 700 natural disasters worldwide almost every year [4].
While destructive natural events are rare in many countries, others are particularly vulnerable to disasters and weather extremes. In particular, countries in high-risk regions of Africa, South America, and Asia or areas along the coasts are repeatedly threatened by disasters such as floods, droughts, earthquakes, and tsunamis. In Africa, in particular, long periods of drought pose a significant threat to the population, while hurricanes and earthquakes are more frequent in Central America and Asia.
How should the government deal with natural disasters?
Natural disasters are a disturbing reality. Regardless of our beliefs, these disasters, such as earthquakes and floods, significantly impact our lives in all parts of the world. Year after year, people around the world face various disasters. Many of these people’s lives are completely devastated by these disasters.
Often people are dissatisfied with the actions of their governments. Many believe that they have paid into the government coffers through their tax payments and that the government should now bail them out in their hour of need.
Governments around the world seem unable to live up to these expectations. It has always been that way, even if you look at the historical record. Governments rarely contribute to natural disasters of any kind. Private charities and religious institutions seem to have the most significant impact during such events. For this reason, every time such a disaster occurs, the role of government is questioned.
Why can’t the government provide economic services?
Natural disasters cause significant damage. People lose their homes, business premises, and other livelihoods. Even the working population faces severe income losses. This is because economic activity is severely affected during this time.
As a result, many people are on the streets and have to fend for themselves. These are the people who are expecting help from the government. They need food, shelter, and clothing to make a living until the situation returns to normal. These supplies are sometimes referred to as “economic services” in the context of disaster relief.
However, it is essential to understand that the government structure is not designed to provide financial services to affected people.
The problem of knowledge: First, relief efforts require much local knowledge. The team providing relief should ideally be decentralized. Decision-making should be quick to ensure that aid reaches those affected promptly. Governments do not work this way.
Every decision made by the government must be documented. Therefore, the decision-making process is centralized. Such a process is highly time-consuming. Therefore, private charities like the Red Cross are much better able to provide these services.
The problem of corruption: in addition, the people who work with charities like the Red Cross want to contribute to the cause voluntarily. They get involved out of passion and tend to donate without ulterior motives. On the other hand, government officials are compelled to contribute to disaster relief. In many parts of the world, government officials are also notorious for their corruption. For this reason, organizations like the Red Cross are better suited to provide economical services.
So what should the government do?
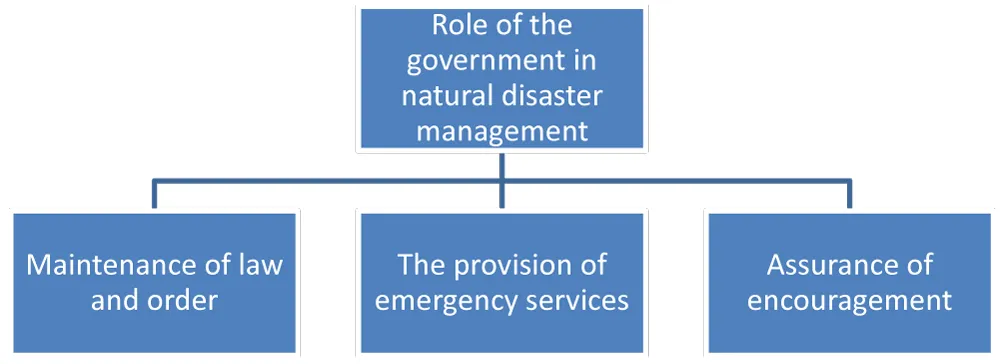
The government also has a precise role in disaster management. Some actions must be taken reactively, i.e., after a disaster, whereas others must be handled proactively.
Maintenance of law and order: It must be clear that natural disasters are also traditionally times when law and order are upset. That is because an earthquake or flood throws the entire area into chaos. This is a reasonable time for anti-social elements to carry out their activities.
The security of citizens is then threatened. At this point, the government can intervene. It must ensure that the military, police, and navy are deployed in large numbers in areas affected by natural disasters.
Ensuring law and order is very important to reduce people’s problems. Most governments around the world do this with success. Citizen groups, however, often do not appreciate these efforts.
Providing rescue services: The government is also the best equipped to provide rescue services. The government and its agencies therefore must conduct rescue operations. The government has all the equipment needed to perform such functions.
Sometimes people need to be located before they can be rescued. Government can perform these tasks better than private entities. For this reason, most governments worldwide can successfully conduct rescue operations.
Encouraging insurance: Governments cannot and should not pay for damage to private property. They must, however, encourage people to manage their finances in the event of natural disasters. This can be accomplished by encouraging private insurance.
The governments should make a certain level of insurance compulsory. They also need to provide tax relief to those who choose more comprehensive insurance (Figure 2).
On balance, it is not economically feasible for the government to assume all responsibility in the event of a natural disaster. Thus, the government should continue to do what it is good at, while private charities should take on tasks where they have a competitive advantage [5].
Conclusion
By developing preparedness plans, recognizing and responding to crises, and implementing recovery measures, the local community plays an important role in identifying hazards. Local community leaders and local health care providers (such as general practitioners, nurses, midwives, pharmacists, and community health workers) can establish credibility, disseminate knowledge, and identify vulnerable people.
The concept and practice of systematic disaster risk reduction. A few examples of these efforts include reducing the factors that lead to vulnerability, reducing exposure of people and property, managing land and the environment, and improving preparedness for the impacts of disasters, to name a few. Reducing disaster risk includes disaster management, disaster prevention, and disaster preparedness and is also a part of sustainable development. Efforts to reduce disaster risk are very important in all areas of life. Though disasters are inevitable, it is very important to optimize risk reduction efforts so that society can recover immediately in the event of a disaster.
- Tropics | National Geographic Society. Available from: https://www.nationalgeographic.org/society/
- Chen X, Li H, Lucero-Prisno DE. Abdullah AS, Huang J, Laurence C, et al. What is global health? Key concepts and clarification of misperceptions. glob health res policy. 2020;5:14. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s41256-020-00142-7
- Weather-related disasters increase over the past 50 years, causing more damage but fewer deaths. Available from: https://public.wmo.int/en/media/press-release/weather-relat . . .
- Natural Disasters: Mitigating Impact, Managing Risks; Nicole Laframboise and Boileau Loko; IMF Working Paper 12/245; 2012. Available from: https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/wp/2012/wp12245.pdf
- How the Government Should Manage Natural Disasters (managementstudyguide.com). Available from: https://www.managementstudyguide.com/government-should-manage-natural-disasters.htm
Article Alerts
Subscribe to our articles alerts and stay tuned.
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 Save to Mendeley
Save to Mendeley
