Archives of Clinical Hypertension
Case report of optimizer implantation to modulate cardiac contractility in patients with chronic heart failure and atrial fibrillation
1Department of X-ray Surgical Methods of Diagnosis and Treatment, University Hospital, Bashkir State Medical University, Ufa, Russia
2Division of Cardiology, University Hospital, Bashkir State Medical University, Ufa, Russia
3Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, University Hospital, Bashkir State Medical University, Ufa, Russia
Author and article information
Cite this as
Pushkareva AE, Blagodarov SI, Abdrakhmanov RE, Plotnikova MR, Dolganov AA, et al. (2023) Case report of optimizer implantation to modulate cardiac contractility in patients with chronic heart failure and atrial fibrillation. Arch Clin Hypertens. 2023; 9(1): 001-003. Available from: 10.17352/ach.000032
Copyright License
© 2023 Pushkareva AE, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.A cardiac contractility modulation device is a new treatment used in patients with heart failure. CCM therapy is associated with an increase in physical activity tolerance, improved quality of life, reduced hospitalizations due to heart failure, and reverse remodeling of the left ventricle in patients with systolic heart failure. In this case, the clinical benefit of cardiac contractility modulation in a patient with chronic heart failure, atrial fibrillation and postinfarction left ventricle aneurysm was reported. Development of postinfarction left ventricle aneurysm in patients with reduced ejection fraction is associated with a high risk of surgical complications. However, an adequate assessment of the functional reserve of the left ventricle myocardium and the choice of surgical correction method allows for receiving favorable outcomes of surgery. We present a case of a successful combination of interventional and surgical treatment of a patient with heart failure and post-infarction left ventricular aneurysm.
Heart Failure (HF) is a serious and growing problem in public health worldwide. According to multicenter international studies, 1% - 2% of the population has HF. Despite the stable incidence, the prevalence of HF is increasing due to the aging of the population, increasing the prevalence of concomitant diseases in the diagnosis of HF. In various countries, more than 10% of all healthcare costs for cardiovascular pathology fall on the treatment of chronic heart failure and a further increase in these costs is predicted [1].
Cardiac contractility modulation is an application of high-amplitude pulses that do not cause cell excitation during the absolute refractory period of the ventricles. Early studies on isolated cardiomyocytes have shown that a stimulus applied during the absolute refractory period through electrodes located inside and outside the cell increases the entry of Ca2+ through the cell membrane and improves the contractility of cardiomyocytes [2]. As part of a prospective randomized FIX-HF5 trial including 160 patients, it was shown that implantation of this device is safe and associated with an increase in peak oxygen consumption 24 weeks after implantation [3].
Aneurysm of the left ventricle is one of the most severe persisting complications after acute transmural myocardial infarction. The main problems in the surgery of postinfarction cardiac aneurysms are high hospital mortality, severe diastolic and systolic dysfunction of the left ventricular myocardium after surgery and recurrent heart failure [4]. Important aspects of determining indications for surgery include comprehensive diagnostic examination, assessment of the functional reserves of the myocardium, and preoperative calculation of the volume of the left ventricle. An excessively radical correction can lead to a pathological decrease and deformation of the left ventricle, a decrease in stroke volume, and a deterioration in systolic and diastolic function, which is clinically manifested by severe heart failure [5]. We present a case of a successful combination of interventional and surgical treatment of a patient with heart failure and post-infarction left ventricular aneurysm.
Case presentation
A 43-year-old male patient was admitted to the University Hospital on 16.11.2021. The patient’s complaints were episodes of rapid heartbeat, accompanied by dizziness, sharp weakness and pre-fainting conditions. From anamnesis: the patient had a posterior myocardial infarction with the transition to the septum wall of the left ventricle 7 months before the admission. Coronary angiography with balloon angioplasty of the right coronary artery was performed on 04.06.2021. The patient had NYHA class 2 HF, aneurysm of the lower wall of the left ventricle with thinning to 0.3 cm. Concomitant diagnosis: type 2 diabetes mellitus, insulin-consuming. The patient was consulted by a cardiac surgeon. Conservative treatment, echocardiography and repeat consultation in 6 months were recommended. The patient regularly took medications: spironolactone 50 mg, sacubitril/valsartan 25 mg x 2 times a day; ticagrelor 90 mg x 2 times a day; atorvastatin 20 mg at night; dapagliflozin 10 mg 1 time a day; Cordarone 200 mg x 2 times a day; bisoprolol 2.5 mg a day.
Previous hospitalizations: 1) From 25.09.2021 to 01.10.2021 the patient was hospitalized at the cardiac center due to HF and paroxysm of stable ventricular tachycardia 25.09.2021.
2) From 02.11.2021 to 12.11.2021, he was hospitalized with the same diagnosis with severe weakness, episodes of loss of consciousness, and blood pressure of 80/60 mmHg. On ECG - paroxysmal ventricular mo monomorphic tachycardia with a heart rate of 196 per minute.
A subcutaneous cardioverter-defibrillator was implanted (17.11.2021). Implantation of a cardiac modulating device Optimizer Smart was performed on 21.12.2021. The patient has not experienced any device-related complications. The patient notes the activation of the subcutaneous cardioverter-defibrillator repeatedly in January - February 2022.
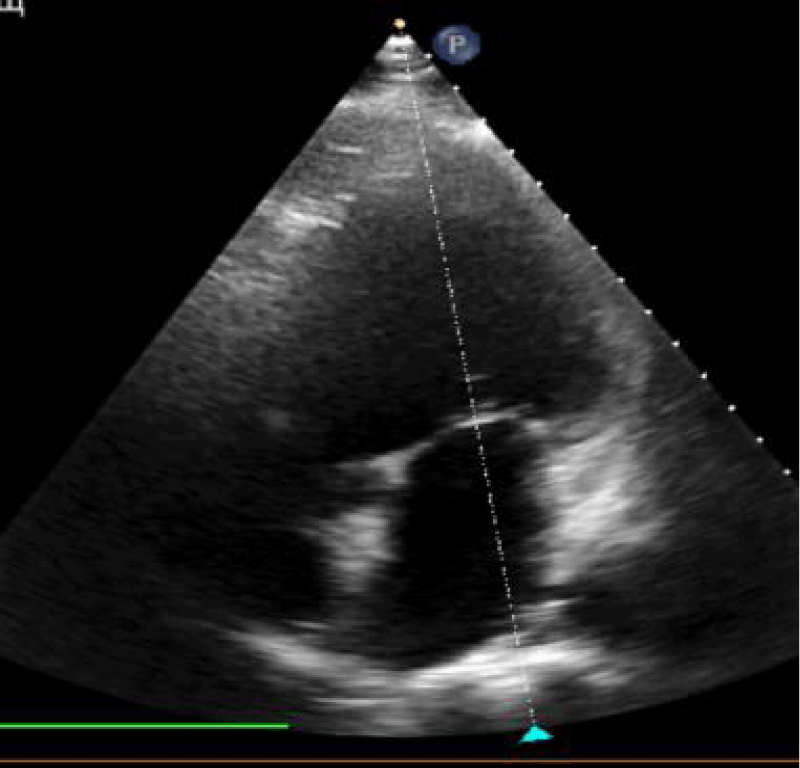
The patient was hospitalized at the Department of Cardiovascular Surgery in the University Hospital on 16.02.2022 with complaints of shortness of breath, episodes of palpitations not related to physical activity and aching pains in the heart area irradiating to the interscapular region. By echocardiography: end-diastolic volume 180 ml, end-systolic volume 96 ml, end-diastolic diameter 6.08 cm, end-systolic diameter 4.5 cm, ejection fraction 32%. An aneurysm of the basal part of the posterior wall of the left ventricle (0.3 cm thick) was detected and the threat of aneurysm rupture was revealed (Figure 1).
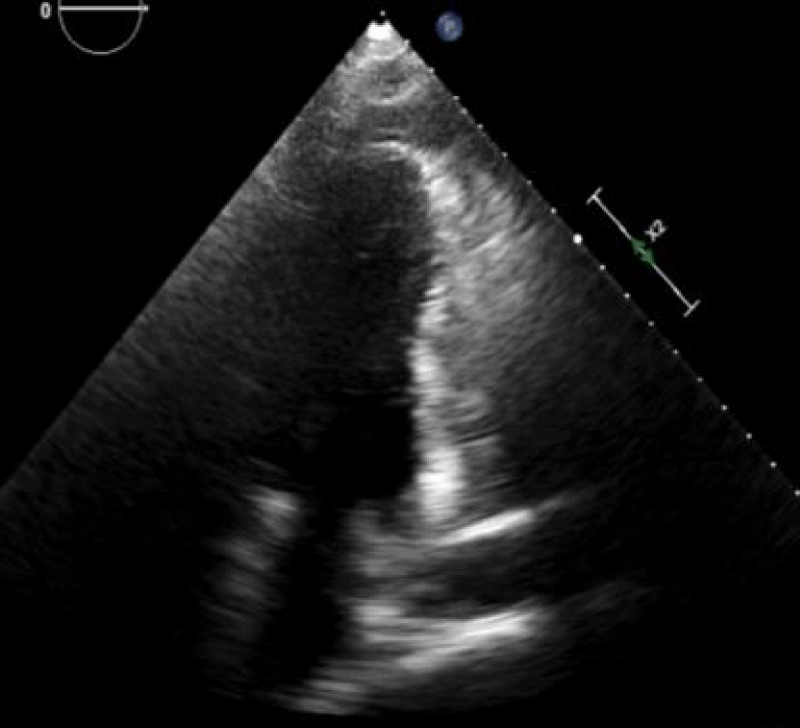
Coronary angiography was performed. Blood flow type was left. No significant atherosclerotic lesions were detected. 17.02. 2022 - modified DOR Procedure (left ventricular reconstruction was performed. By echocardiography after the surgery (Figure 2): end-diastolic volume 165 ml, end-systolic volume 80 ml, end-diastolic diameter 5.8 cm, end-systolic diameter 4.2 cm, ejection fraction 48%, separation behind the tip of pericardium 0.6 cm, behind the lateral wall and right ventricle of 0.7 cm, behind the posterior wall - 0.8 cm.
During 1 year follow-up no major adverse cardiac events were registered which shows the efficacy of the performed treatment.
Conclusion
The development of atrial fibrillation in patients with HF significantly worsens the prognosis of the course of the disease and increases mortality from all causes. There have been several independent clinical observations on the use of Optimizer Smart in patients with atrial fibrillation [6]. The present case clearly shows that the cardiac contractility modulation device should be considered the device of choice in patients with symptoms of heart failure with reduced ejection despite the use of optimal drug therapy. The introduction of a new generation of cardiac contractility modulators Optimizer Smart into clinical practice is a promising direction in the treatment of patients with chronic HF and atrial fibrillation who do not have indications for cardiac resynchronization therapy. One of the important clinical tasks in patients with atrial fibrillation and implanted cardiac contractility modulators is the control of heart rate, therefore proper prescription of antiarrhythmic drugs such as amiodarone and beta-blockers should be considered. In previous clinical trials the effectiveness in improving the clinical condition, functionality and quality of life, as well as the prevention of hospitalizations in patients with symptoms of heart failure has been demonstrated [7-9]. In order to understand the capabilities of modulating devices in patients with HF and atrial fibrillation, it is necessary to conduct full-fledged clinical studies.
Ethics statement
The patient provided his written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Funding
The work was funded by the Russian science foundation № 21-75-00065.
- Writing Group Members; Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, Das SR, de Ferranti S, Després JP, Fullerton HJ, Howard VJ, Huffman MD, Isasi CR, Jiménez MC, Judd SE, Kissela BM, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Liu S, Mackey RH, Magid DJ, McGuire DK, Mohler ER 3rd, Moy CS, Muntner P, Mussolino ME, Nasir K, Neumar RW, Nichol G, Palaniappan L, Pandey DK, Reeves MJ, Rodriguez CJ, Rosamond W, Sorlie PD, Stein J, Towfighi A, Turan TN, Virani SS, Woo D, Yeh RW, Turner MB; American Heart Association Statistics Committee; Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2016 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016 Jan 26;133(4):e38-360. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000350. Epub 2015 Dec 16. Erratum in: Circulation. 2016 Apr 12;133(15):e599. PMID: 26673558.
- Wood EH, Heppner RL, Weidmann S. Inotropic effects of electric currents. I. Positive and negative effects of constant electric currents or current pulses applied during cardiac action potentials. II. Hypotheses: calcium movements, excitation-contraction coupling and inotropic effects. Circ Res. 1969 Mar;24(3):409-45. doi: 10.1161/01.res.24.3.409. PMID: 5766519.
- Abraham WT, Lindenfeld J, Reddy VY, Hasenfuss G, Kuck KH, Boscardin J, Gibbons R, Burkhoff D; FIX-HF-5C Investigators and Coordinators. A randomized controlled trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of cardiac contractility modulation in patients with moderately reduced left ventricular ejection fraction and a narrow QRS duration: study rationale and design. J Card Fail. 2015 Jan;21(1):16-23. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2014.09.011. Epub 2014 Oct 5. PMID: 25285748; PMCID: PMC4390995.
- Kaneyuki D, Kohno H, Matsuura K, Ueda H, Matsumiya G. Left Ventricular Aneurysm After Post-Infarction Ventricular Septal Defect Repair. Ann Thorac Surg. 2019 Apr;107(4):e263-e265. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2018.08.078. Epub 2018 Oct 22. PMID: 30359591.
- Benetis R, Vaskelyte J, Raugeliene R, Ereminiene E, Jankauskiene L. Ankstyvosios komplikacijos, kairiojo skilvelio geometrijos bei tūrio pokyciai po dvieju tipu skilvelio formos ir tūrio rekonstrukcijos: randines sienos kompresijos ir modifikuotos Doro aneurizmektomijos [Early complications and changes of left ventricular geometry and volume following two types of ventricular reconstruction: compression of scar zone and modified Dor aneurysmectomy]. Medicina (Kaunas). 2004;40 Suppl 1:35-8. Lithuanian. PMID: 15079098.
- Liu M, Fang F, Luo XX, Shlomo BH, Burkhoff D, Chan JY, Chan CP, Cheung L, Rousso B, Gutterman D, Yu CM. Improvement of long-term survival by cardiac contractility modulation in heart failure patients: A case-control study. Int J Cardiol. 2016 Mar 1;206:122-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.01.071. Epub 2016 Jan 6. PMID: 26788686.
- Anker SD, Borggrefe M, Neuser H, Ohlow MA, Röger S, Goette A, Remppis BA, Kuck KH, Najarian KB, Gutterman DD, Rousso B, Burkhoff D, Hasenfuss G. Cardiac contractility modulation improves long-term survival and hospitalizations in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. Eur J Heart Fail. 2019 Sep;21(9):1103-1113. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1374. Epub 2019 Jan 16. PMID: 30652394.
- Kloppe A, Lawo T, Mijic D, Schiedat F, Muegge A, Lemke B. Long-term survival with Cardiac Contractility Modulation in patients with NYHA II or III symptoms and normal QRS duration. Int J Cardiol. 2016 Apr 15;209:291-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.02.001. Epub 2016 Feb 3. PMID: 26908357.
- Abraham WT, Kuck KH, Goldsmith RL, Lindenfeld J, Reddy VY, Carson PE, Mann DL, Saville B, Parise H, Chan R, Wiegn P, Hastings JL, Kaplan AJ, Edelmann F, Luthje L, Kahwash R, Tomassoni GF, Gutterman DD, Stagg A, Burkhoff D, Hasenfuß G. A Randomized Controlled Trial to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of Cardiac Contractility Modulation. JACC Heart Fail. 2018 Oct;6(10):874-883. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2018.04.010. Epub 2018 May 10. Erratum in: JACC Heart Fail. 2023 Jan;11(1):132. PMID: 29754812.
Article Alerts
Subscribe to our articles alerts and stay tuned.
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 Save to Mendeley
Save to Mendeley
